Overview
Enabling mev-commit on your relay is simple and requires minimal changes to your existing setup.
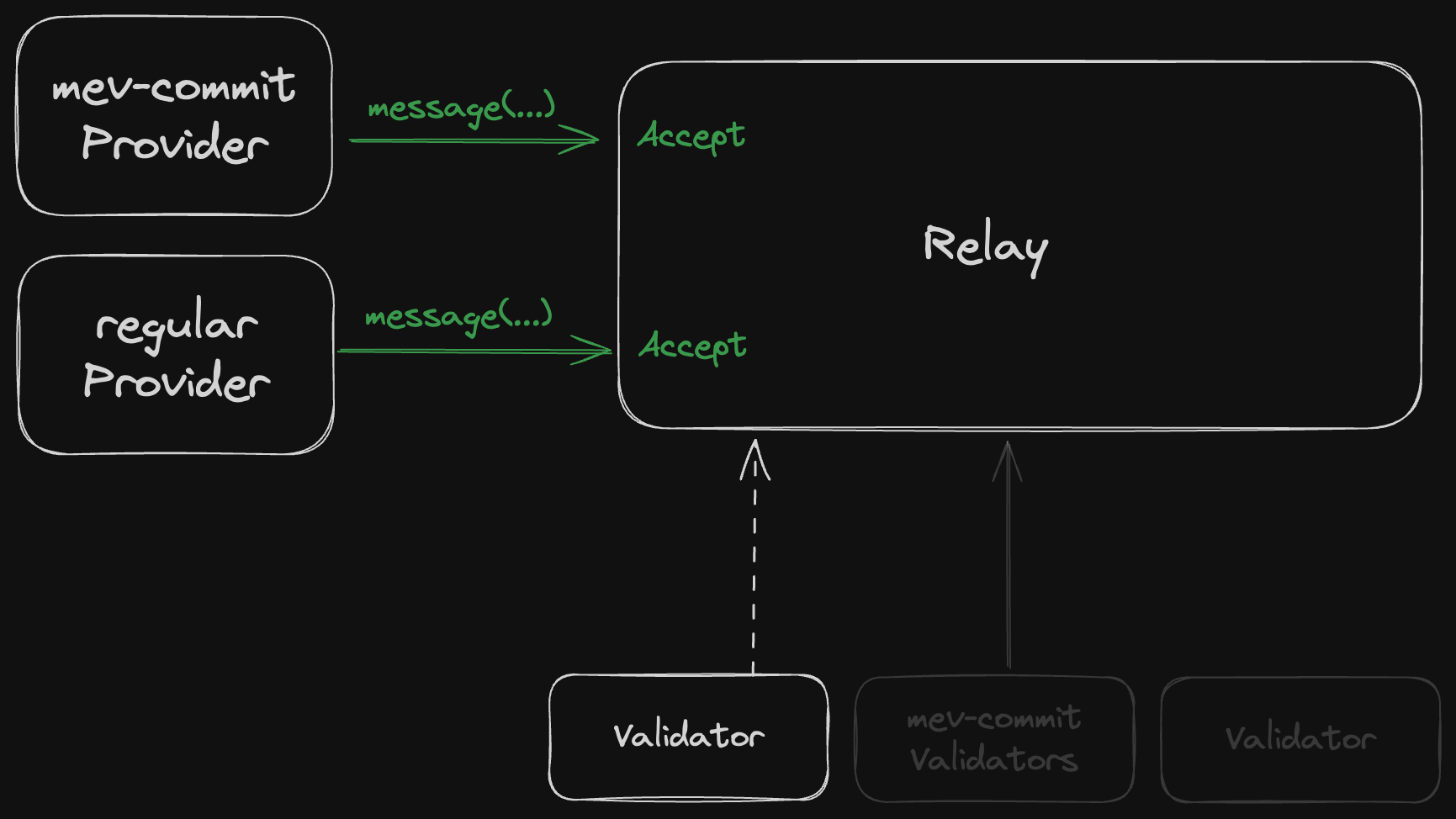
- If they haven’t opted in, your relay works normally:
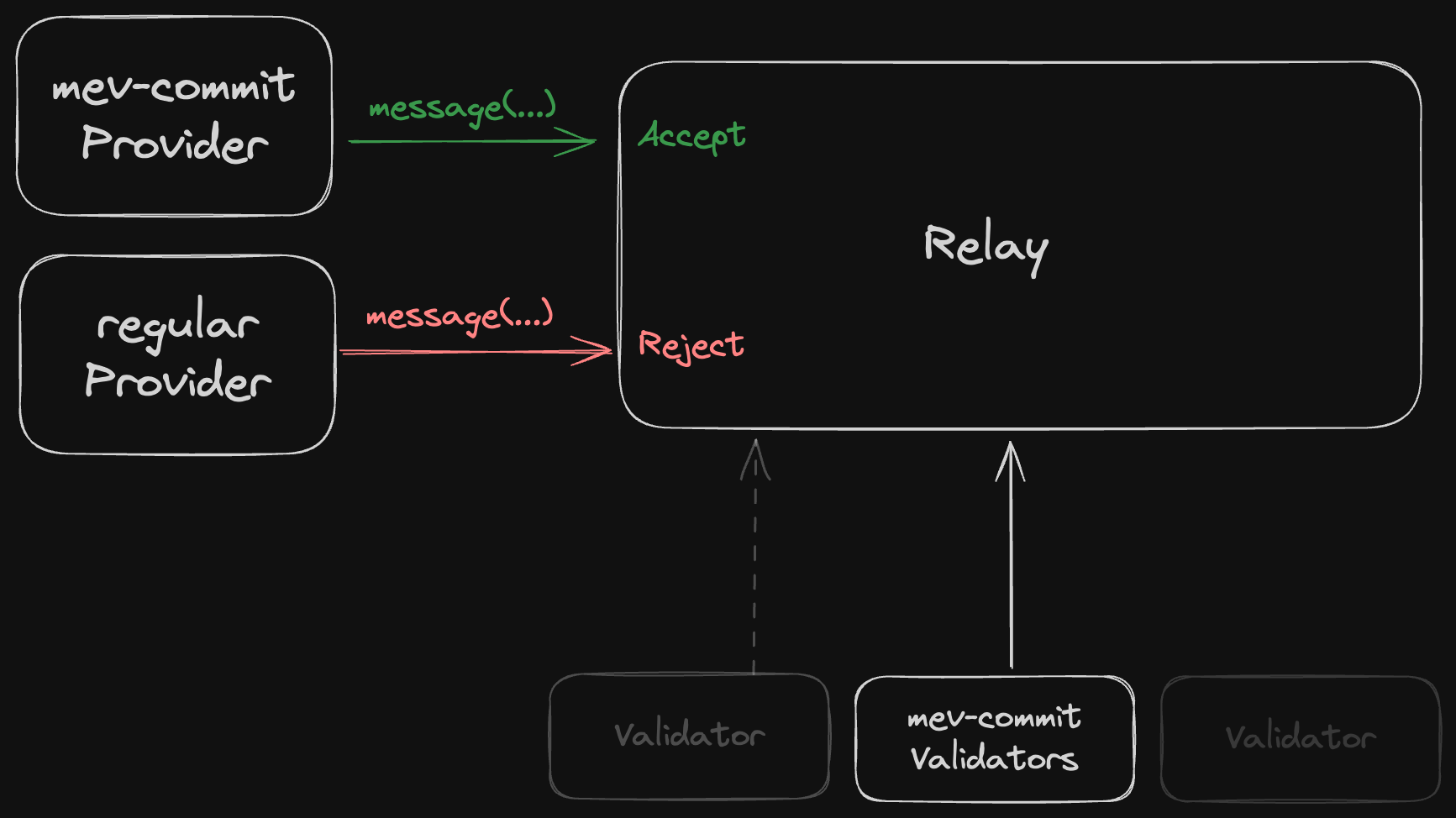
- If they have opted in, your relay only accepts blocks from mev-commit builders:
- Provider Registry: Lists opted-in builders and their BLS keys
- Validator Registry: Shows which validators have opted into mev-commit
Quick Start
View the Example Implementation
- Check out this mev-commit relay integration
- Add required environment variables:
Test and Deploy
Test filtering behavior on Holesky:
- Register a test builder
- Submit test bids
- Verify correct block filtering
Register Your Relay
- Add your relay to our supporting relays list
- Provide connection details for validators
- Contact the Primev team to coordinate validator outreach
Implementation Details
What Contracts to Monitor
To track which validators have opted into mev-commit, you’ll want to monitor the following contracts:-
Validator Registry Router on Ethereum L1:
- Network: Ethereum Mainnet
- Address:
0x251Fbc993f58cBfDA8Ad7b0278084F915aCE7fc3
-
Provider Registry on mev-commit-chain:
- Network: mev-commit
- Address:
0x1C2a592950E5dAd49c0E2F3A402DCF496bdf7b67
How to Query the Provider Registry
The mev-commit provider registry contract maintains the list of authorized providers such as block builders. You can query this contract to validate builder addresses. Contract Details:- Network: mev-commit-chain
- Address:
How to query the registry for connected providers
How to query the registry for connected providers
You can retrieve all connected providers using the following script:
Expected Output
Expected Output
The output will be a list of providers, identified by their BLS pubkey, that have registered with mev-commit.
Mainnet Integration
Mainnet Contracts

